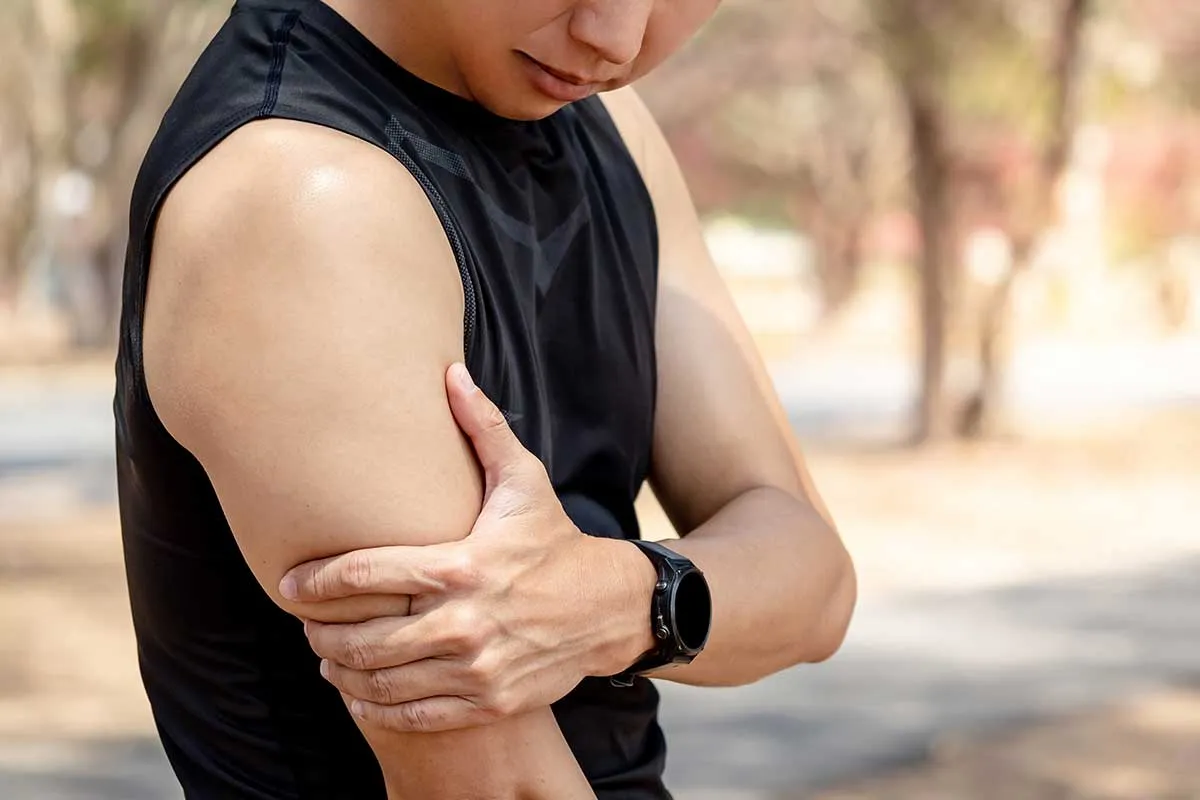

Biceps tendinitis (tendinopathy) describes an overload condition of the biceps tendon, which attaches the biceps muscle to the shoulder. The biceps muscle is one of the two main muscles in the front of the upper arm. It is responsible for bending the elbow and rotating the forearm, to turn the palm upwards.
Biceps tendinitis is commonly diagnosed in athletes and people who participate in activities that require repetitive overhead movements.
Contact Us 020 8004 6659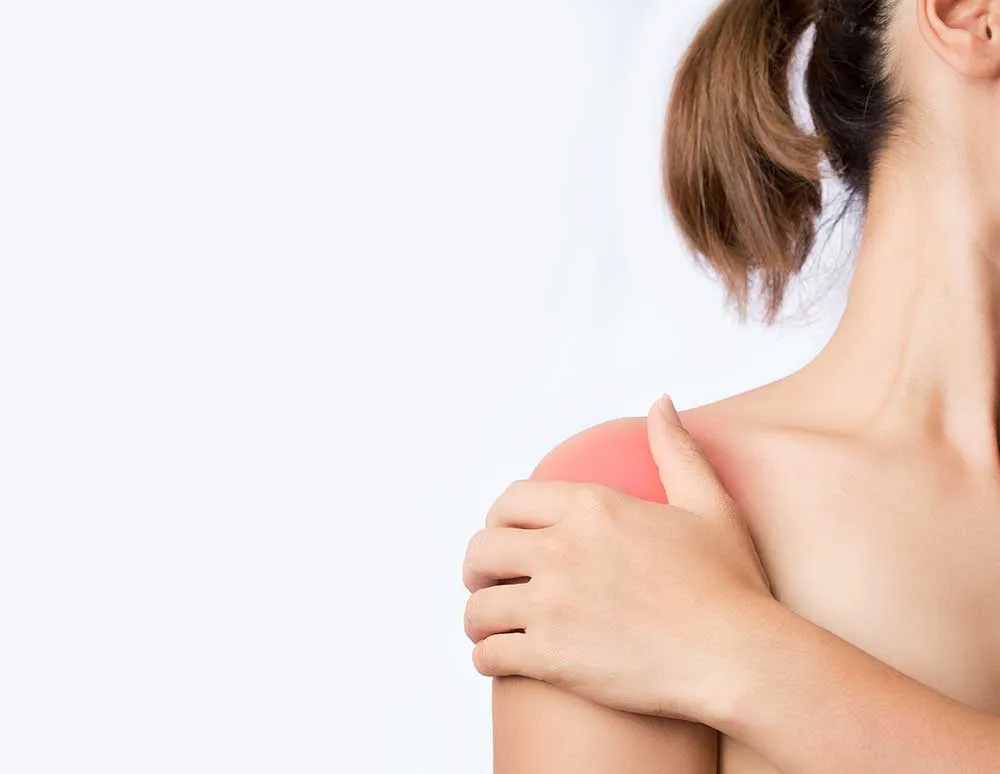
Biceps tendinitis can affect people of all ages, but it is most common in adults in their 40s and 50s. It is also more common in people who:
Participate in activities that require repetitive overhead movements, such as tennis, baseball, and swimming
Have a history of shoulder injuries
Have diabetes
Are overweight or obese
The main symptom of biceps tendinitis is pain in the front of the shoulder. The pain may be worse with activity, especially activities that involve overhead lifting or reaching. Other symptoms of biceps tendinitis may include:
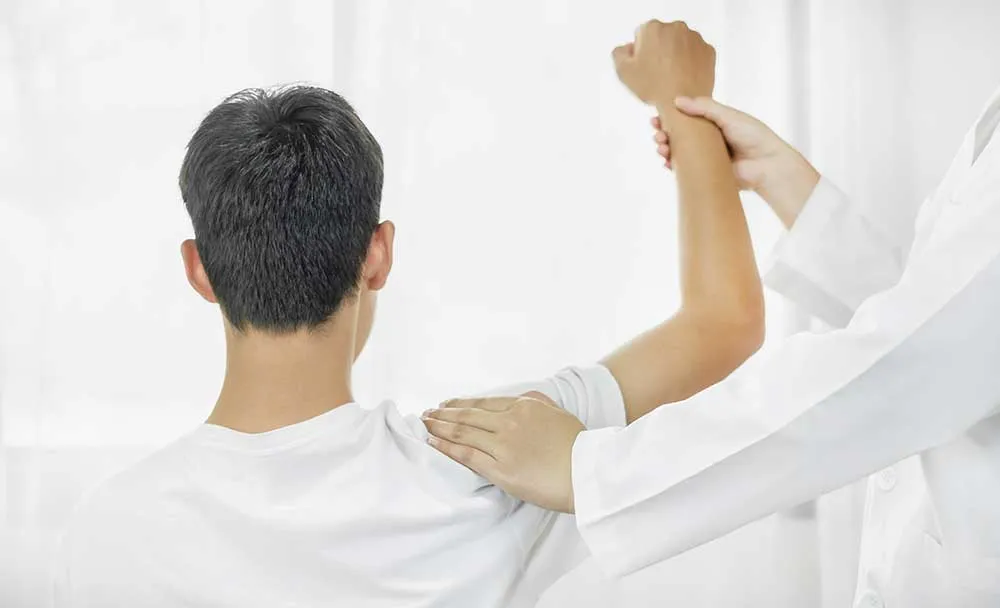



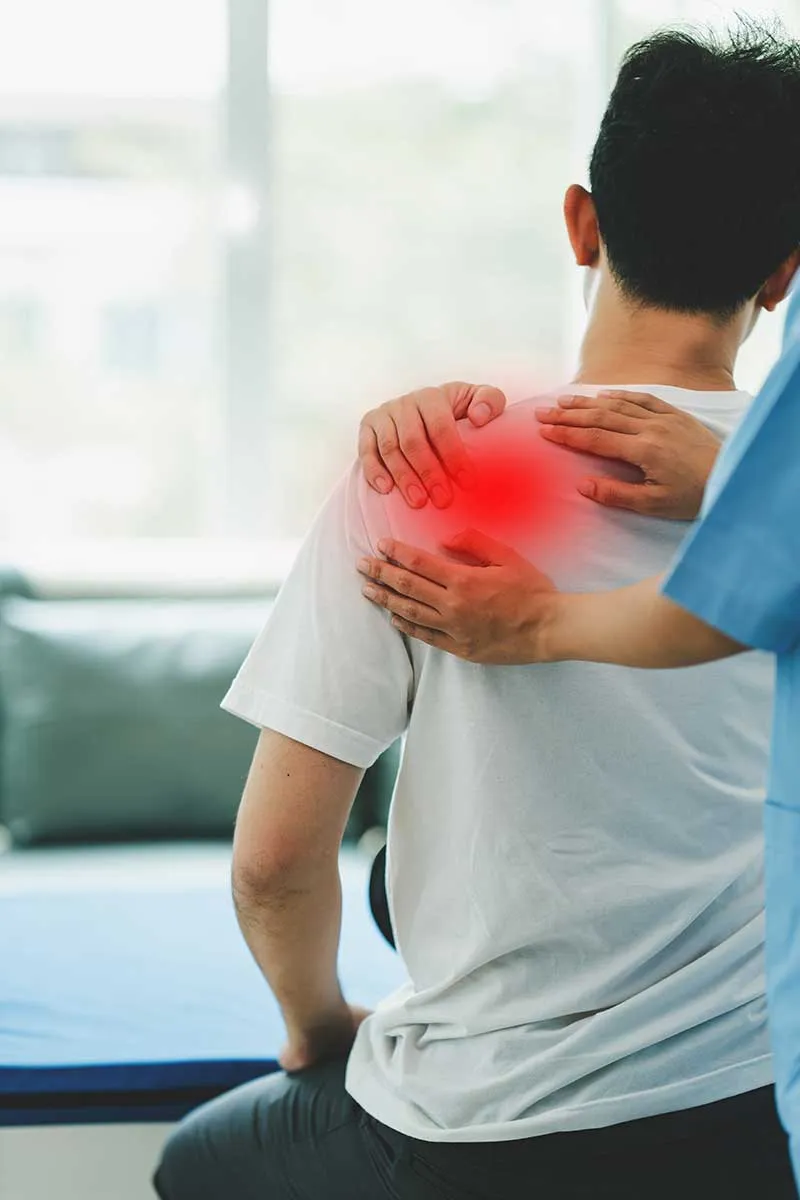
The diagnosis of biceps tendinitis is usually made based on the patient's medical history and physical examination. The doctor will ask about the patient's symptoms and activities. The doctor will also examine the shoulder for pain, localised tenderness, and assess range of motion limitations. Imaging tests, such as X-rays, ultrasound or MRI scans, can help to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other causes of shoulder pain.
Contact Us 020 8004 6659Treatment for biceps tendinitis typically focuses on relieving pain and inflammation. Non-surgical treatments are often effective. Non-surgical treatments may include:
At The Joint Injection Clinic, these injections are performed after a thorough consent process, whereby the risk and benefits of the procedure are discussed in detail with your doctor. The experienced medical doctor will then place you in a seated or lying position. The front of the shoulder is cleaned using a cleaning solution to ensure that the procedure is performed under sterile conditions. Local anaesthetic is injected from the skin to the tendon sheath under ultrasound guidance. After giving the local anaesthetic a few minutes to take effect, the tendon sheath injection is performed with a small dose of steroid and local.
The injection itself is normally completed within 30-60 seconds, after which a plaster is applied and post-injection advice is given. The patient is advised to look out for any signs of infection, specifically to check whether the local area becomes red, hot, tender, swollen or if they develop a fever. If this occurs then the patient is asked to contact the clinic immediately at which time a formal reassessment will occur and if needed oral antibiotics can be prescribed. The patient is also warned that following any injection they may notice a short-term worsening or flare in their symptoms after the local anaesthetic has worn off (4-5 hours). This may last for 3-5 days and the patient is advised to consider icing of the area using an ice pack for 10-15 minutes every hour as required.
If non-surgical treatments are not effective, surgery may be an option.
The best treatment option for you will depend on the severity of your biceps tendinitis, your overall health, and your activity level.
If you are experiencing pain and stiffness in your shoulder, it is important to see a doctor to get a diagnosis and discuss treatment options. With early diagnosis and treatment, most people with biceps tendinitis can recover fully and return to their normal activities.